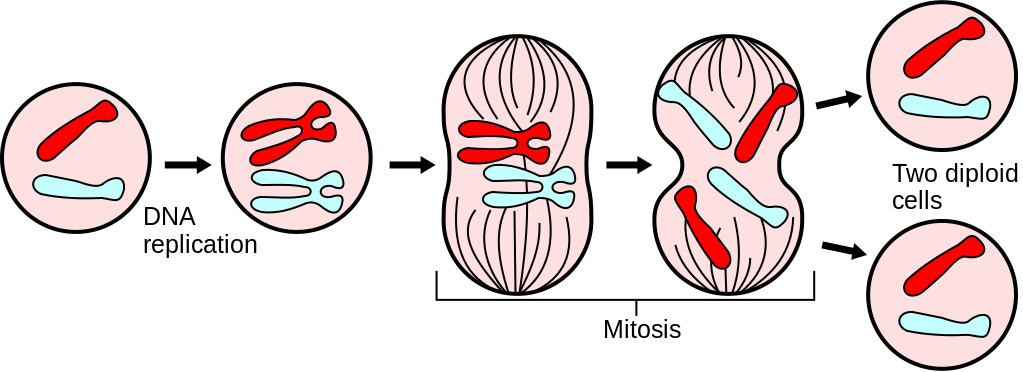
Mitosis is the
process by which body cells divide to make new cells. Each daughter cells will be identical to the
parent cell.
Stages of Mitosis
Interphase- Before S Phase
The cell is performing its day-to-day
activities (such as being a liver cell or a stomach cell). The cell is also preparing for mitosis, or
cell division. Chromosomes will be found
as long threads called chromatin.
Interphase- After S Phase
Chromosomes, which are made of DNA,
undergo a process called replication, which creates two copies of the genetic
material. The S in S-Phase stands for synthesis, the process by which DNA
copies itself. The cell is now ready to
begin mitosis.
Mitosis- Prophase
Chromatin in the nucleus begins to
condense and X-shaped chromosomes appear.
The nuclear membrane dissolves so that chromosomes can move around the
cell. The centrioles move to opposite
ends of the cell and spindle fibers start to appear.
Mitosis- Metaphase
The spindle apparatus fully develops. Spindle
fibers line the chromosomes up in the middle of the cell. When
metaphase is complete, there will be a neat row of chromosomes at the equator
of the cell.
Mitosis- Anaphase
Spindle fibers shrink to pull the
chromosomes apart. One sister chromatid
moves to each pole of the cell. Both
sides of the cell have a full copy of the genetic material.
Mitosis- Telophase
A complete set of chromosomes can be found at
each pole of the cell. The chromosomes uncoil
into chromatin. The cell begins to
divide into two daughter cells. The nuclear membrane begins
to reappear.