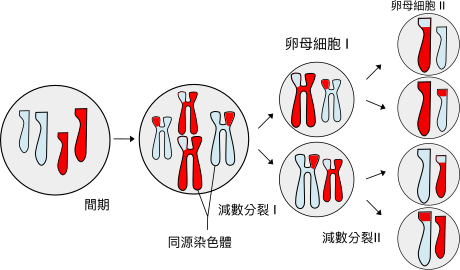
Meiosis is the
process by which reproductive cells are formed.
The cell will divide twice before stopping. Each new cell will contain
only half of the number of chromosomes as the parent cell and will be
genetically different from all of the other daughter cells.
Stages of Meiosis
Interphase: G1 phase- Before DNA
Replication
The reproductive cell grows in size. It is also performs all of the day-to-day
tasks of a healthy cell. This phase is called the G1 phase, because G stands
for gap.
Interphase: S phase- After DNA
Replication
The chromosomes have undergone DNA replication
(or synthesis) to make an extra copy of the DNA. The rod- shaped chromosomes become X-shaped;
each half of the X is called a ‘sister chromatid.’
Phophase I
The condensed chromosomes undergo a
process called ‘crossing over’ where they exchange DNA. The spindle fiber network begins to appear
and centrioles move to the poles of the cell.
Metaphase I
The chromosomes move to the center of
the cell and line up randomly. Each
chromosome has spindle fibers attached to the center which help move it around
the cell.
Anaphase I
The spindle fibers shrink, pulling
entire chromosomes to the either side of the cell. At the end of anaphase, each side of the cell
will have half of the chromosomes from the cell.
Telophase I
Each side of the cell is now
haploid, it has half of the genetic material of the original cell. The cytoplasm begins to divide into two and
two daughter cells are formed.
Prophase II
The nuclear membrane breaks up again
as the spindle network appears. The
chromosomes do not replicate and there is no crossing over in Prophase II.
Metaphase II
The chromosomes line up in the center
of the cell. The spindle fibers connect
the centrioles to the centromere of each chromosome.
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids separate and move to
opposite poles of the cell. Each sister
chromatid is now considered to be a full chromosome.
Telophase II
The nuclei reform and the cell divides
into two. At the end of the telophase II
there will be a total of 4 cells, each with half of the original number of
chromosomes.
No comments:
Post a Comment